EGGS AND SPERM
EGGS AND SPERM
Eggs
(ova) and sperm have half the number of chromosomes of normal body cells. They
are called haploid cells rather than diploid cells. A single egg cell is called
an ovum. Collectively, eggs and sperm are called gametes or sex cells. When fertilization
occurs, an egg (ovum) and a sperm fuse to form a zygote.
EGGS AND SPERM HAVE
SEVERAL IMPORTANT ADAPTATIONS LINKED TO THEIR STRUCTURE.
EGGS
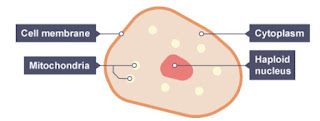
An egg
cell (ovum) is one of the largest cells in the human body and can just be seen
without using a microscope.
-
Has
a haploid nucleus - containing only half the number of chromosomes of a normal
cell nucleus
-
Has
a large cytoplasm- which contains the nutrients for the developing embryo.
-
Many
mitochondria- needed for mitosis (cell division) after fertilization.
-
Has
a special cell membrane- which only allows one sperm to fertilize it.
SPERM
Has a
haploid nucleus- containing only half the number of chromosomes of a normal
cell nucleus
Has a
tail (for motility)- which propels it through the cervix, uterus and oviducts
towards the egg.
Has many
mitochondria (where respiration occurs)- to release the energy needed for its
journey towards the egg.
Have
special enzymes in a structure called called acrosome, which break through the
cell membrane of the egg during fertilization.

Comments
Post a Comment