Explain how structures of the human ear are adapted to their functions. (20 marks)
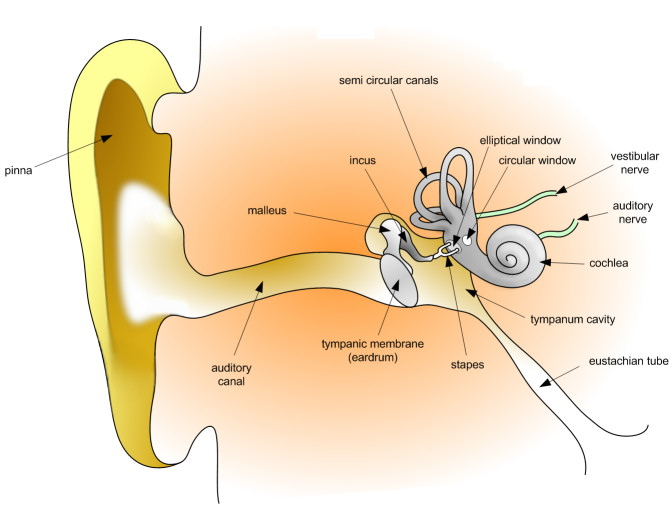
- The pinna;- is funnel shaped to trap sound waves; cartilaginous to maintain the funnel shape; collects and directs sound waves into the external auditory meatus ear;
- The external auditory canal; - a tube connected to the pinna that directs sound waves from the pinna to the eardrum lining the auditory canal; has hair that trap foreign particles;
- The canal contains wax-secreting cells; and hair which traps dust particles; and pathogenic bacteria hence prevent them from getting into the ear;
- The eardrum; - has a thin tough membrane; that easily vibrates when hit by sound waves; transferring them into vibrations.
- The ear ossiscles; - they act like a layer and they easily move forward and backward to amplify sound vibrations that hit them;
- The suspensory ligaments; - suspends the ear ossicles and prevents excessive vibration that would otherwise damage the inner parts of the ear;
- The eustachian tube - it connects the middle ear with the pharynx; and it equalises air pressure between the middle and the outer ear so as to prevent distortion of the eardrum;
- The oval window;- has thin membrane that transmits sound vibrations into the endolymph;
- The cochlea;- highly coiled to occupy a small area but to accommodate a large number
- of sensory cells;
- The perilymph and endolymph; - these are fluids that absorb mechanical shock; hence protect the delicate\parts in the inner ear; They also transmit vibrations to the inner parts of the ear;
- The sensory cells; - when stimulated, they generate nerve impulses; which are transmitted by the auditory nerve to the brain;
- The semi-circular canals; - these are tubular cavities that maintains body balance and posture; they contain special cells that are sensitive to changes in gravity;
Nice..
ReplyDeleteThank You for pointing out great work.
DeleteThanks
DeleteThanks! :-)
ReplyDeleteThank you
ReplyDeleteThat's great work which is well analysed.
ReplyDeleteMay you answer this please,'' Explain how the mammalian skin is adapted to its functions.
great work splendid
ReplyDeletereally helpful
ReplyDeletethank you great work
ReplyDeleteThank you
ReplyDeleteGreat work
ReplyDeleteThanks for your explanations
ReplyDeleteThanks 👌
ReplyDeleteGreat word....thank you
ReplyDeleteNice post
ReplyDeleteDr. Sanjay Sachdeva is one of the best ENT specialist in Delhi Consult with ENT Doctor in Delhi. Get consultation for ear,sleep disorder, nose & throat disorders, and Cochlear Implant