Describe the structure and function of the mammalian ear in relation to hearing and balance
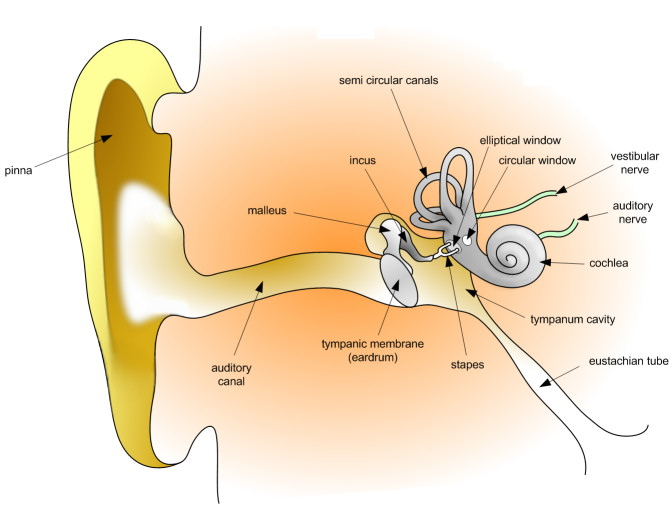
- The ear has the pinna which is funnel shaped to collect/direct sound waves into the ear;
- The ear has the external auditory canal; a passage through which sound waves pass to reach the ear drum/tympanic membrane;
- The ear-drum/tympanic membrane is thin and tight to convert sound waves into (sound) vibration and transmit them to the ear ossicles;
- The ear ossicles are three tiny bony structures that vibrate when struck; by the ear-drum; the ear ossicles amplify and transmit sound vibration to the oval window;
- The inner ear has the cochlea; which is long and spiral/coiled increasing surface area for attachment of many sensory cells that detect sound vibrations; the sensory cells in the cochlea together with the basilar membrane form the organ of corti;
- Sensory cells in the cochlea/the organ of corti, are stimulated by the vibration received from the oval window; the perilymph and endolymph fluids; Impulses are generated and transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve fibres; for interpretation.
- The inner ear has three semi-circular canals arranged in planes at right angles to each other; to be able to detect changes in the position of the body in any of the planes;
- The semi-circular canal has a swelling at its base called the ampulla; ampulla has sensory cells which detect any changes in the head displacement;
- The inner ear has the utriculus, sacculus and has a gelatinous cupula; which has otolith attached to the sensory cells; Any movement of body causes the otolith to change position thus exerting pressure on the sensory cells which causes the generation of impulses ; impulses are transmitted to the brain for interpretation along the vestibular nerve fibres; the position of the body (in relation to gravity ) is interpreted.
Comments
Post a Comment